Ferritin is essentially your body’s iron pantry. When levels dip under 30 ng/mL, hair follicles often slip into a resting phase, and you might spot extra strands on your brush. Keeping an eye on ferritin helps you catch trouble before thinning becomes obvious.
Ferritin And Hair Loss Overview
Here’s a quick look at how different ferritin ranges affect your hair—and what you can do next.
Ferritin Level Thresholds And Recommended Actions
Below is a snapshot of common ferritin values, their impact on hair health, and the recommended next steps.
| Ferritin Level ng/mL | Hair Health Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Below 20 | High shedding risk | Start iron supplements and diet tweaks |
| 20–50 | Mild thinning | Monitor diet and retest in 3 months |
| Above 50 | Supports growth | Maintain balanced iron intake |
Use this as a springboard for a deeper look at your iron status.
The diagram below from Wikipedia illustrates ferritin’s hollow shell, showing how it stores iron atoms for later use.
Next Steps And Resources
- Focus on iron-rich foods like spinach, lentils, and lean red meat
- Pair iron sources with vitamin C to boost absorption
- Recheck ferritin after 8–12 weeks of dietary changes or supplementation
For a sense of what normal hair shedding looks like, compare your daily counts against our guide: How Much Daily Hair Loss Is Normal.
Understanding Ferritin And Hair Growth

Think of ferritin as a piggy bank for your body’s iron. When a hair follicle needs energy and building blocks for cell division, it makes a withdrawal.
Those 100,000 follicles on your scalp work like tiny factories around the clock. If iron reserves drop, production slows and hairs slip early into the telogen (resting) phase—so you notice more shedding.
- Anagen (Growth): Follicles fire on all cylinders with good iron reserves.
- Catagen (Transition): A dip in iron slows down the machinery.
- Telogen (Resting): Iron shortages push follicles into rest prematurely.
How Ferritin Stores Iron
Under the hood, ferritin proteins wrap iron atoms in a secure shell, shielding the body from free-radical damage. This clever package gives us the most reliable snapshot of total iron stores.
A ferritin level below 30 ng/mL often signals insufficient iron for robust hair growth.
Dive deeper into Hair Growth Cycle at PRP For HairLoss to see how ferritin levels align with each phase.
Monitoring ferritin helps you decide when to tweak your diet or add supplements, laying the groundwork for smarter testing, interpretation, and treatment strategies.
How Ferritin Levels Impact Hair Health
Researchers consistently find that low ferritin pushes hair follicles toward a resting state, leading to more shedding. It’s not just about anemia—iron stores themselves determine whether follicles stay in growth mode.
Here’s what the data shows:
- An average deficit of 18.5 ng/mL in ferritin nudges follicles closer to telogen (rest).
- Nearly 50% of participants fell below 30 ng/mL, even without classic anemia signs.
- Hair follicles rely on iron reserves to sustain the anagen (active growth) stage.
Key Study Takeaways
Even a mild dip in ferritin can trigger extra shedding. In one case, a man increased his ferritin from 22 ng/mL to 55 ng/mL and saw noticeably fuller hair within four months.
Low ferritin is like sprinting on an empty tank—it robs hair cells of the stamina they need to thrive.
Multiple large-scale reviews show low iron storage is a common feature in nonscarring hair loss. A systematic analysis of 10,029 participants reported a mean ferritin shortfall of −18.51 ng/mL, with up to 50% under 30 ng/mL in certain regions. Learn more on source.com.
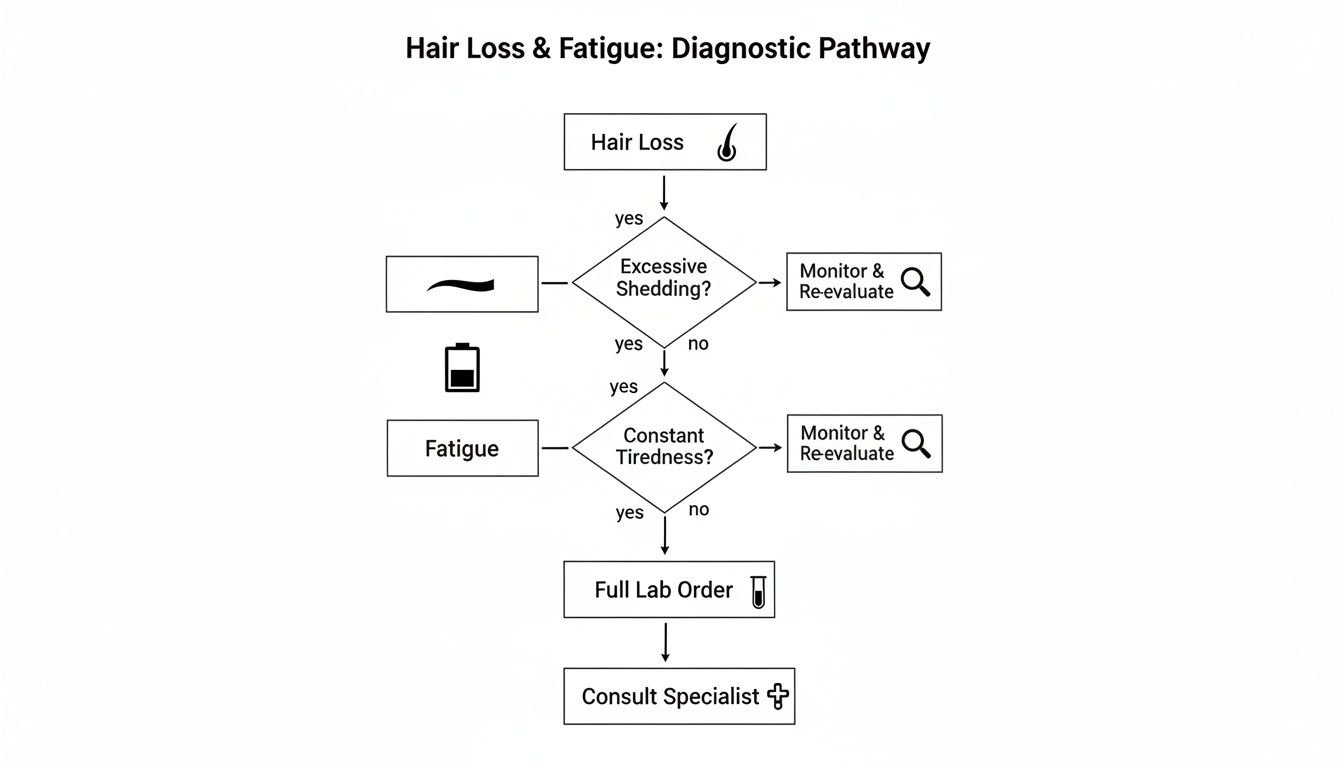
Spotting Symptoms And Ordering Lab Tests
Hair loss doesn’t always start on your head. Sometimes your body flashes warning lights before you notice thinning.
Imagine climbing stairs and feeling winded, or seeing your nails split at the slightest knock. Those are clues that hair follicles might already be in the resting phase.
- Persistent fatigue despite enough sleep
- Brittle or spoon-shaped nails
- Pale or sallow skin tone
- Diffuse thinning across the scalp
Many dermatologists now include ferritin in their workup for diffuse hair loss. Adding a ferritin test can reveal iron-store depletion in 27.9% of cases that would otherwise go unnoticed. Read the full research on iron-store depletion on Wiley Online Library.
Expert Tip: When you request blood work, mention both diffuse thinning and unexplained fatigue.
For a practical baseline, check out how to tell if your hair is thinning.
Request Comprehensive Iron Panel
Use this checklist to make sure you get the right labs:
- Describe your symptoms and ask for serum ferritin plus a full iron panel
- Review results (target >50 ng/mL) and schedule a retest in 8–12 weeks
Interpreting Ferritin Results for Healthy Hair
Your ferritin level—think of it as your iron savings account—can tell you a lot about hair health. Levels above 50 ng/mL usually signal ample fuel for growth, while 30–50 ng/mL is a cue to fine-tune nutrition and keep an eye on trends.
Dropping below 30 ng/mL often means it’s time to introduce iron supplements or lean into iron-rich foods. Remember, inflammation and markers like CRP can inflate ferritin readings, so your provider will look at the full picture before recommending a plan.
- Above 50 ng/mL: Optimal environment for strong, healthy hair
- 30–50 ng/mL: Moderate risk—adjust nutrition and monitor levels
- Below 30 ng/mL: High risk—start supplements and schedule follow-up labs
Imagine a patient feeling drained, whose ferritin comes back at 28 ng/mL. In that case, most clinicians would start a tailored iron regimen and plan a follow-up in 6–8 weeks.
This diagram lays out a clear path: spot symptoms, order ferritin and CRP tests, interpret results, then take action.
Ferritin Ranges Risk And Management Guidelines
To help you and your clinician move quickly from lab report to treatment, here’s a handy reference:
| Ferritin Range ng/mL | Hair Loss Risk | Suggested Management |
|---|---|---|
| Above 50 ng/mL | Low | Maintain balanced diet and routine blood-work |
| 30–50 ng/mL | Moderate | Increase iron-rich foods; retest in 6–8 weeks |
| Below 30 ng/mL | High | Begin iron supplementation and schedule follow-up labs |
These thresholds reflect consensus from clinical studies linking ferritin status to hair growth. Always review numbers alongside symptoms and other markers like CRP before finalizing any treatment plan.
For a deeper dive into lab interpretation, check out How to Read Blood Test Results.
Managing Low Ferritin To Stop Shedding

Rebuilding your iron stores starts at the kitchen table. Focus on everyday foods and straightforward supplements rather than complicated regimens. Over time, this approach helps tame the extra hairs on your pillow.
Begin with these nutrient powerhouses:
- Lean Red Meat loaded with heme iron for fast absorption
- Beans & Lentils paired with citrus fruits for a vitamin C boost
- Fortified Cereals served with bell peppers for improved uptake
Don’t overlook hidden causes if levels stay low. Heavy periods, gut issues like celiac disease, or chronic blood loss can all steal your iron. A quick chat with your doctor can uncover these culprits.
Step-By-Step Protocol
- Get a baseline ferritin test and note the ng/mL value.
- Adopt iron-focused meals and log your plate for 8–12 weeks.
- Introduce 30–100 mg of elemental iron daily, adjusting for tolerance.
- Retest to confirm at least a 20–30 ng/mL boost.
| Phase | Ferritin Level (ng/mL) |
|---|---|
| Baseline | 20 |
| After 3 Months | 60 |
In one example, a patient lifted her ferritin from 20 ng/mL to 60 ng/mL in three months by following this plan. Pairing these gains with PRP sessions often unlocks even more visible regrowth. For meal ideas, see our hair loss diet guide.
Managing Tolerance
Some people feel mild stomach upset when they start iron pills. If that happens:
- Split the dose into two smaller servings
- Take supplements with a snack or meal
This simple tweak keeps you on track without missed doses. Aim to recheck your ferritin every 3–6 months and stay above 50 ng/mL.
Consistent iron management works like an engine tune-up, keeping hair follicles fueled.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Ferritin Measure And Why Does It Matter For Hair
Ferritin is like your body’s iron bank account, storing the fuel your follicles need to grow. When ferritin dips too low, hair cells can’t divide quickly, and thinning sets in.
Imagine follicles as plants. Without an iron reserve, they struggle to sprout new shoots. Results vary by person, but maintaining that “bank balance” gives your hair the best shot at staying strong.
How Often Should I Test Ferritin When Treating Hair Loss
Most specialists suggest retesting every 3–6 months while you boost levels above 50 ng/mL. Once you’re comfortably past that mark, an annual check usually suffices.
If you notice new symptoms or adjust your diet and supplements, feel free to test sooner. Staying flexible helps catch dips before they affect your hair.
Are Iron Supplements Safe And Which Form Should I Choose
- Ferrous Bisglycinate: Gentle on the stomach and easy to absorb.
- Starting Dose: 30–60 mg elemental iron, ideally with vitamin C.
- Side Effects: Mild nausea or constipation—if they occur, try adjusting timing or splitting doses.
- Tip: Always take iron with a meal to boost absorption and ease discomfort.
When To See A Specialist
If hair shedding comes with fatigue, dizziness, or—on the women’s side—heavy periods, it’s time to call a dermatologist or hematologist. They can run tests for malabsorption or chronic blood loss and uncover hidden issues.
When symptoms extend beyond shedding, professional insight can prevent long-term thinning.
Regular follow-ups keep your plan on track. As your ferritin climbs and hair regrows, you’ll gain confidence in fine-tuning each step.
Ready to take control of your hair health? Explore treatment options and professional guidance at PRP For HairLoss.

Leave a comment