Thinking about starting a new treatment for hair loss, especially one as powerful as oral minoxidil, naturally brings up questions about the potential downsides. Let's be straight about it: the most common side effects are unwanted hair growth (hypertrichosis) and a temporary bout of hair shedding. Less frequently, people might experience things like dizziness or a bit of fluid retention.
The good news? These issues are almost always linked to the dosage you're taking, which means they are something you and your doctor can easily get a handle on.
Decoding the Risks: A Balanced Overview
Taking a new medication can feel a bit like setting out on a new trail. You want a map that shows you the beautiful views ahead but also points out any tricky spots you might encounter. Oral minoxidil is a lot like that. It's an incredible tool in the fight against hair loss, but getting the full picture—including the potential side effects—is the key to moving forward with confidence.
Minoxidil's journey to becoming a hair loss hero was actually a happy accident. It was first developed as a powerful medication for high blood pressure. Doctors quickly noticed an interesting side effect: their patients were growing more hair. This history is precisely why some of its side effects are cardiovascular in nature.
But here’s the crucial difference: the doses used for hair loss today are a tiny fraction of what was used to treat hypertension. This "low-dose" approach has been a total game-changer, letting us get the hair growth benefits while dramatically lowering the risk of other issues.
What the Data Shows
To put all this in perspective, let's look at the numbers from actual clinical studies. This isn't about guesswork; it's about what real patients have experienced.
This chart gives you a quick visual of what to expect and how often.
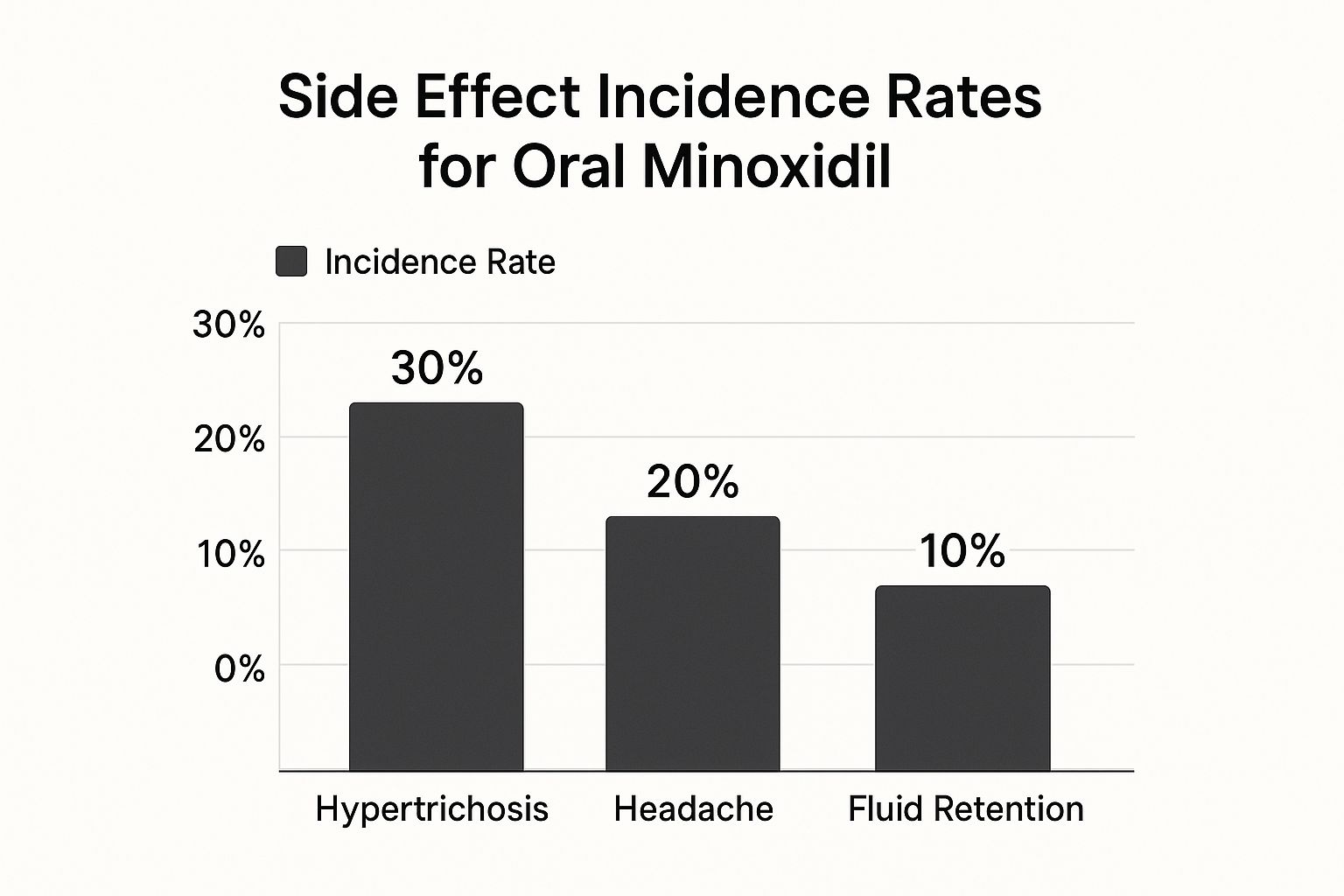
As you can see, unwanted hair growth is the most common flag raised, while things like fluid retention are much further down the list.
For a more detailed breakdown, this table organizes potential side effects by how frequently they pop up, giving you a handy reference guide.
Quick Look at Oral Minoxidil Side Effects by Frequency
| Side Effect Category | Specific Side Effects | What You Need to Know |
|---|---|---|
| Most Common (Reported in >10% of users) | Hypertrichosis (unwanted hair growth on face/body) | This is the most frequent side effect, hands down. It's dose-dependent and typically reversible by lowering the dose or stopping the medication. |
| Common (Reported in 1-10% of users) | Temporary Hair Shedding (Telogen Effluvium) | Often happens 2-8 weeks after starting. This is a good sign the medication is working, pushing out old hairs to make room for new ones. |
| Lightheadedness or Dizziness | A result of minoxidil's blood-vessel-widening effect. It's usually mild and often fades as your body gets used to it. | |
| Fluid Retention (Edema) | Mild swelling, typically in the ankles or feet. Your doctor can manage this, often by adjusting the dose. | |
| Uncommon to Rare (<1% of users) | Tachycardia (Increased Heart Rate) | A sensation of a rapid or fluttering heartbeat. It's important to report this to your doctor right away. |
| Pericardial Effusion | Fluid accumulation around the heart. This is a very rare but serious side effect, mainly seen with the high doses once used for hypertension. | |
| Postural Hypotension | A sudden drop in blood pressure when you stand up, which can cause dizziness. More likely in people with pre-existing low blood pressure. |
This table helps show that while there's a range of potential effects, the really serious ones are quite rare, especially at the low doses prescribed for hair loss.
Understanding the "Why" Behind the Effects
So, what’s actually happening inside your body to cause these reactions? Minoxidil is a vasodilator, which is just a fancy way of saying it opens up your blood vessels. This boosts blood flow, which is fantastic for waking up sleepy hair follicles on your scalp.
But since you're taking a pill, that effect isn't just on your head—it's systemic, meaning it circulates through your entire body. This is the big difference between oral minoxidil and the topical foam or liquid.
The key takeaway here is that side effects are often just an extension of the drug's main job. Better circulation can sometimes lead to temporary lightheadedness or fluid retention as your body adjusts.
This systemic action is also why oral minoxidil can be a lifesaver for people who got zero results from topical versions. For anyone battling hair thinning from conditions like what androgenic alopecia is, getting the medication delivered effectively through the bloodstream can finally tip the scales in their favor.
At the end of the day, it's all about balancing the incredible potential for hair regrowth with a risk profile that is well-understood and highly manageable. Now, let’s dig deeper into each specific side effect so you know exactly what to look for.
The Most Common Side Effect: Unwanted Hair Growth

Let's get right to it and talk about the side effect you're most likely to run into with oral minoxidil: extra hair sprouting in places you didn't ask for it. The clinical term is hypertrichosis, but it really just means fine, light-colored hairs popping up on the forehead, cheeks, arms, or even your back.
While that might sound a little strange, it makes perfect sense when you understand how the drug works. Oral minoxidil is a systemic medication, meaning it travels through your entire bloodstream. It can't just target the hair follicles on your scalp; its growth-promoting signals go everywhere.
Think of it like watering your lawn with a big, wide-spraying sprinkler. You’re aiming for the grass, but you know some of that water is going to hit the flowerbeds and the pavement. Same idea here. Minoxidil’s main job is to wake up scalp follicles, but other dormant follicles on your body might get a little sprinkle of that magic, too.
How Often Does This Actually Happen?
So, how common is it really? This isn't some rare, shocking outcome; it's the most frequently reported side effect by a long shot.
One of the largest studies on low-dose oral minoxidil for hair loss, involving over 1,400 patients, gives us a very clear picture. It found that hypertrichosis showed up in 15.1% of patients. While that number might seem high, it's important to put it in context: other side effects were far less common, and only a tiny 1.2% of people stopped the treatment for any reason. You can dig into the full study results on how common oral minoxidil side effects are in large patient groups.
This data is actually pretty reassuring. It tells us that while unwanted hair is the most likely hurdle, it's manageable enough that the vast majority of people stick with the treatment, happy with the results on their head.
For a lot of guys, a bit of extra hair on the arms or a fuller beard is a welcome bonus. In fact, it's a common question whether you can grow more facial hair using Rogaine, and many see this systemic effect as a potential perk.
Practical Ways to Manage Unwanted Hair
If you do notice hypertrichosis and you're not a fan, don't sweat it. The new hairs are usually very fine and light—often just "peach fuzz"—and dealing with them is straightforward.
Here are the go-to strategies:
- Dose Adjustment: This is the easiest and most effective first move. Unwanted hair growth is very dose-dependent. A small reduction in your daily dose is often all it takes to make the extra hair fade, usually without messing with your scalp results.
- Hair Removal: For any hair that does appear, simple, standard methods work just fine. Trimming, shaving, waxing, or dermaplaning are all great options, depending on where the hair is.
- Give It Time: Sometimes, your body just needs a few months to get used to the medication. You might find that the effect lessens on its own over time.
And remember, this side effect is completely reversible. If you decide to stop taking oral minoxidil, any extra hair on your face or body will go away.
The Shedding Phase: A Good Sign in Disguise
Another very common—and often alarming—experience is an initial increase in hair shedding right after you start. Seeing more hair in the shower drain can be downright scary, but it's crucial to understand that this is actually a positive sign.
This initial shed, known as telogen effluvium, typically kicks in between weeks two and eight. It happens because minoxidil is actively waking up your dormant hair follicles. To make room for new, thicker, healthier hairs, the follicles first have to push out the old, weaker hairs that were on their way out anyway.
It's like renovating a garden. Before you can plant beautiful new flowers, you have to pull out all the old weeds and dead plants. This shedding phase is just your scalp clearing the deck for a much better growth cycle. It's temporary, and it’s one of the best indicators that the medication is doing exactly what it's supposed to.
Understanding Cardiovascular Side Effects

It’s completely understandable to have questions about heart-related side effects, especially once you learn that oral minoxidil started its life as a potent blood pressure medication. That history is exactly why we talk about things like lightheadedness, a faster heart rate, or fluid retention.
But context is everything. The low doses used for hair loss are a world away from the high doses once used for hypertension.
Think of your circulatory system like a network of pipes. Minoxidil is a vasodilator, meaning it gently widens those pipes. This allows more blood, oxygen, and nutrients to flow through—which is exactly what wakes up dormant hair follicles.
Of course, widening the pipes can cause a slight dip in the overall pressure. Your body, being the smart system it is, might speed up your heart rate just a tad to compensate and keep everything balanced. This simple, adaptive response is behind most of the cardiovascular effects people sometimes notice.
From High-Dose Medication to Low-Dose Hair Treatment
It's crucial to draw a thick line between the side effect profile of high-dose minoxidil for severe hypertension and the low-dose oral minoxidil (LDOM) used for hair loss today. The doses prescribed for hair are often 10 to 40 times lower than what was used to treat blood pressure.
This dramatic dose reduction is the single biggest reason why significant cardiovascular issues are now so uncommon.
The goal with LDOM isn't to overhaul your blood pressure; it's simply to give your circulation a gentle nudge to support hair growth. For most healthy people, the cardiovascular system barely registers the change. The key is awareness, not alarm.
Lightheadedness and Dizziness
The most common cardiovascular effect is a feeling of lightheadedness, especially when you stand up too quickly. Doctors call this postural hypotension. It happens because the widened blood vessels cause a brief dip in blood pressure before your body has a chance to catch up.
This feeling is usually mild and tends to go away on its own within a few weeks as your body gets used to the medication. An easy fix? Just get up a little more slowly from a chair or from bed.
Fluid Retention and Tachycardia
Less frequent are fluid retention (edema) and a faster-than-normal heart rate (tachycardia). Edema usually appears as mild swelling in the ankles or feet, while tachycardia can feel like your heart is fluttering or racing.
Both are simply signs of your body compensating for the vasodilation. So, just how common are they?
A large-scale safety study from 2020 looked at 1,404 patients on low-dose treatment and gave us some solid numbers.
- Lightheadedness occurred in just 1.7% of patients.
- Fluid retention was seen in 1.3%.
- Tachycardia was reported by only 0.9%.
These numbers are incredibly reassuring. They confirm that for the overwhelming majority of people, the cardiovascular effects of low-dose oral minoxidil are minor and manageable.
Being well-informed about medication safety is always a smart move. To get a broader perspective on how different medications can impact the heart, it can be helpful to learn about common drugs that can cause QT prolongation and other heart risks. This kind of knowledge empowers you to have a more thorough conversation with your doctor.
While these systemic effects are rare, they're still important to watch for. That’s why your doctor will go over your medical history, paying close attention to any pre-existing heart conditions or low blood pressure, before writing a prescription. This careful screening is what makes the treatment a safe and effective choice for the right person.
Oral vs. Topical Minoxidil Side Effects

When it comes to minoxidil, choosing between a pill and a liquid often feels like picking between two different routes to the same destination. Both can get you to impressive hair regrowth, but the journey—and the potential bumps along the way—are quite different. The core of that difference comes down to one simple concept: local vs. systemic.
Topical minoxidil is a targeted mission. You apply the foam or solution directly to the area you want to treat. Think of it like a spot treatment for a single struggling plant in your garden. Because it’s applied right where it's needed, the side effects are almost always confined to that specific patch of skin.
Oral minoxidil, on the other hand, is a systemic treatment. Taking a pill sends the medication coursing through your entire bloodstream. This is more like watering the whole garden at once—it’s powerful, but it affects everything, not just the one plant you were focused on. This is why the side effect profile shifts from scalp issues to potential body-wide effects.
The Trade-Off: Scalp Irritation for Systemic Risks
For many people, the biggest frustration with topical minoxidil isn't that it fails to work, but that it’s just so difficult to tolerate day in and day out. The formulas, especially the liquid version which often contains propylene glycol, are infamous for causing scalp irritation.
Here's what people often complain about with topical solutions:
- Itching and Redness: This is the most common issue by far and the reason many people give up.
- Flaking and Dandruff: The alcohol and other carriers can seriously dry out the scalp, leading to a snowstorm on your shoulders.
- Greasy Hair: The residue it leaves behind can be a cosmetic nightmare and a real hassle to deal with every morning.
Oral minoxidil completely sidesteps these problems. With nothing being applied to your scalp, there's zero chance of contact dermatitis or that sticky, greasy feeling. For anyone who has fought a losing battle with an itchy, flaky scalp, this can be a massive quality-of-life upgrade.
But, as with most things, there's a trade-off. By taking the treatment internally, you swap the risk of local skin reactions for the risk of systemic side effects, like the lightheadedness or fluid retention we covered earlier.
A Head-to-Head Comparison in Clinical Studies
So, what does the research say when you put the two forms against each other? The data really highlights this exact exchange between local irritation and systemic effects.
Comparative studies in men with androgenetic alopecia consistently find that systemic side effects are more common with the pill. A key randomized trial showed that hypertrichosis (that's unwanted body hair) was nearly twice as likely in the oral group (49%) compared to the topical group (25%). Headaches also popped up more often for those taking the pill. On the flip side, skin-related problems like itching and eczema were significantly more common among the topical users.
The choice isn't about which option is universally 'safer,' but which set of potential side effects is a better fit for your body and lifestyle. Can you tolerate a bit of scalp maintenance, or would you prefer to manage a low risk of systemic effects?
Understanding this fundamental difference is everything. For a more detailed breakdown of how these two treatments compare in terms of application, lifestyle, and results, check out our guide on oral versus topical minoxidil.
Which Risk Profile Works for You?
At the end of the day, the decision comes down to your personal tolerance and what you can stick with consistently. A treatment is only effective if you actually use it long-term.
Think about your own situation:
- If you have sensitive skin or have already tried topical minoxidil and found it unbearable, the oral form might be the obvious choice.
- If you're someone with pre-existing low blood pressure or have any concerns about cardiovascular effects, the localized nature of topical minoxidil might be more comforting.
This is a conversation to have with your doctor, where you can weigh your medical history against the distinct risk profiles of each option. That way, you can choose the path you can confidently stay on to get the results you're after.
How Doctors Make Minoxidil a Safe Bet for Your Hair
It's one thing to read about the potential side effects of oral minoxidil, but it's another to understand how doctors actually manage them in the real world. This isn't a treatment you're left to figure out on your own. A good doctor has a clear, methodical game plan to get you the best results while keeping any risks incredibly low.
The whole approach is proactive, not reactive. It's all about preventing problems before they even have a chance to start. This partnership between you and your doctor is what allows you to move forward with real confidence.
The "Start Low, Go Slow" Philosophy
The most important strategy in any doctor's toolkit is the "start low, go slow" method. This isn't just a friendly tip; it's the absolute gold standard for prescribing oral minoxidil for hair loss. You won't be started on a high, aggressive dose. Instead, your doctor will begin with a tiny amount.
This initial micro-dose lets your body get used to the medication without any shock to the system. Think of it like dipping your toes in a pool instead of diving headfirst into the deep end. Your body has a chance to gently acclimate to the changes in circulation.
Over the next few weeks or even months, your doctor will keep a close eye on how you're doing. If you're feeling great and not experiencing any issues, they might slowly increase the dosage. The goal is to find that sweet spot: the lowest possible dose that delivers fantastic hair growth with zero problems.
Why Your Medical History Is So Important
Before your doctor even thinks about writing a prescription, they'll need to do a deep dive into your medical history. This is the first and most critical screening tool to spot any red flags that might make oral minoxidil the wrong fit for you.
They'll pay special attention to a few key areas:
- Cardiovascular Conditions: Any history of heart problems, like heart failure, angina, or past heart attacks, is a major consideration.
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension): Since minoxidil's primary function is to lower blood pressure, starting with it already low could make you prone to dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Kidney or Liver Health: These are the organs that process the medication out of your body. Any existing impairment means they have to be extra cautious.
- Other Medications: Your doctor needs a complete list of everything you're taking—prescriptions, supplements, everything—to make sure there are no bad interactions.
This first conversation is a non-negotiable safety check. Be completely upfront and honest here. It helps your doctor make the right call for your health and weeds out anyone who might be at a higher risk of side effects.
A great doctor will always put your overall health far ahead of your cosmetic goals. That detailed medical history isn't just a formality; it's the first line of defense against potential issues.
Ongoing Monitoring Gives You Peace of Mind
Getting your prescription is just the beginning of the journey. Regular follow-up appointments are a built-in part of the safety plan. These check-ins are where you and your doctor track your progress and make sure everything is running smoothly.
During these visits, your doctor will usually do a few things:
- Check Your Vitals: A quick blood pressure and heart rate check is standard practice. This confirms your cardiovascular system is handling the medication just fine.
- Talk About How You Feel: This is your chance to bring anything up. Are you feeling lightheaded at all? Noticing anything new? This conversation allows your doctor to make small adjustments if needed.
- A Quick Visual Check: They'll look for any subtle physical signs of side effects, like swelling in your feet or ankles, and of course, they'll be excited to see how your hair regrowth is coming along.
This ongoing teamwork makes the entire process feel managed and transparent. It's why working with the right professional is so critical. If you're searching for an expert, you can find a list of the best hair loss doctors who specialize in these safety protocols. This careful oversight is what gives you true peace of mind, knowing that any tiny issue will be caught and dealt with right away.
Making an Informed Decision About Your Hair Loss
So, where does this all leave you? Ultimately, deciding to start oral minoxidil is a personal call, one you should make hand-in-hand with your doctor. When you take a step back and look at all the data, the worries about oral minoxidil side effects really boil down to two different buckets.
In one bucket, you have the common, fairly mild, and easily managed issues. In the other, you have the much rarer systemic problems that doctors are specifically trained to screen for and avoid.
For most healthy men, the scale tips heavily toward treatment. You're weighing the very real possibility of significant hair regrowth against a risk profile that's been studied for decades. The most common side effect is often just a bit of unwanted hair elsewhere—which for many is a minor nuisance, and for some, even a welcome sign the drug is working. Plus, it's completely reversible just by tweaking the dose.
Becoming an Active Partner in Your Treatment
With the knowledge from this guide, you can now have a completely different kind of conversation with your doctor. You're not just showing up to get a prescription; you're walking in as an informed, active participant in your own treatment plan.
You're equipped to ask much sharper, more relevant questions:
- "Looking at my personal health history, are there any specific side effects you'd want me to watch for more closely?"
- "What's your typical 'start low, go slow' approach for someone with my profile?"
- "What's the threshold for you? At what point would a side effect make you consider lowering my dose versus stopping the medication altogether?"
This change is everything. It transforms the experience from one of passive hope or anxiety into a proactive, collaborative strategy built on solid science and a clear understanding between you and your physician.
The path forward is one of cautious optimism. It’s about acknowledging that no medication is perfect, but the safety measures around low-dose oral minoxidil are strong and designed with your well-being in mind. You can move forward with confidence, knowing you’ve done the work to understand both the incredible upside and the manageable risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're looking into hair loss treatments, it's natural to have questions. Let's tackle some of the most common concerns about oral minoxidil side effects to give you the clarity you need.
Are the Side Effects of Oral Minoxidil Permanent?
For almost everyone taking low-dose oral minoxidil for hair loss, the side effects are not permanent. They are almost always tied directly to the dose you're taking.
This means if you lower the dose or stop the medication, the side effects typically go away. For instance, the most common side effect is hypertrichosis (a bit of extra body or facial hair). This is completely reversible and those fine hairs will fade after you stop the treatment. The same goes for issues like lightheadedness or minor fluid retention.
Can Oral Minoxidil Cause Chest Pain or Heart Palpitations?
It's a valid question, given minoxidil's history as a blood pressure drug. While cardiovascular effects are possible, they are very rare at the low doses used for hair loss. A feeling of a fast or fluttering heartbeat (tachycardia) has been reported, but in major studies, this happens in less than 1% of patients.
Chest pain is taken very seriously and is an extremely rare side effect. If you ever experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or significant heart palpitations, you need to stop the medication and contact your doctor right away.
This is exactly why doctors perform a thorough medical screening before even considering a prescription. They are careful to rule out patients with pre-existing heart conditions to keep these risks to an absolute minimum.
How Long Does It Take for Side Effects to Appear?
The timing really depends on the specific side effect. Some are quite predictable. The initial shedding phase, for example, usually kicks in 2 to 8 weeks after you start. It's temporary and actually a good sign the medication is starting to work. You can learn more about how soon you can expect Rogaine to work to understand that initial timeline.
Other side effects, like a bit of lightheadedness, might show up in the first few weeks as your body gets used to the medication's effect. Unwanted hair growth (hypertrichosis) is a slower burn and might take a few months to become noticeable.
Do Side Effects Go Away on Their Own?
Many of the milder ones do. It's not uncommon for a little lightheadedness or a mild headache to simply fade away after the first few weeks as your body adjusts.
That said, you should never just ignore a side effect and hope for the best. Always keep an open line of communication with your doctor. They can tell you if what you're feeling is just a normal adjustment or if a small change in your dosage could solve the problem without sacrificing your hair growth results.
Navigating your hair restoration journey requires reliable information and a plan you can trust. At PRP For HairLoss, we provide in-depth resources to help you understand your options and make the best choices for your health and confidence. Learn more at https://prpforhairloss.com.

Leave a comment