If you're seeing your hair thin out at the front, you're not alone. The most common culprit is androgenetic alopecia, a genetic condition you probably know as male pattern hair loss.
This process is fueled by a hormone called dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. Think of DHT as a key that fits a specific lock on the hair follicles along your hairline. When it locks in, it slowly shrinks those follicles, making it harder and harder for them to produce strong, healthy hair. It's an incredibly common part of life for millions of men.
Unpacking Frontal Hair Thinning
It's completely normal to feel a jolt of concern when you first spot changes in your hairline. Is this just a phase? Did I do something to cause this? The truth is, for most guys, the answer is written in their DNA.
The hair follicles at your temples and across the front of your scalp are often genetically wired to be far more sensitive to DHT than the follicles on the back of your head.
Imagine your scalp is a garden. DHT acts like a very specific, slow-moving weed killer that only targets certain plants—in this case, the hair follicles at the front. Over time, it chokes them off, causing the hair they grow to become finer, shorter, and lighter. Eventually, they stop growing anything at all.
This gradual shrinking process is known as miniaturization.
Why Does It Start at the Front?
That classic "M" shaped receding hairline is the signature of male pattern baldness for a reason. The front of your scalp and your temples just happen to have a higher concentration of these DHT-sensitive follicles.
This is why you can have significant thinning up front while the hair on the back and sides of your head stays perfectly thick. It's all about genetic programming. The process is usually slow and steady, often kicking off subtly sometime after puberty.
And this is far from rare. Male pattern baldness is the number one reason for thinning hair in men. In fact, studies show that around 42% of men experience noticeable hair loss, with the frontal region almost always being one of the first places to show it.
It's easy to get worried, but don't mistake this for a sign of poor health. Frontal hair thinning is almost always a cosmetic issue decided by a genetic lottery—it’s not a reflection of your lifestyle or overall wellness.
To help you get a clearer picture, here’s a quick breakdown of the main factors at play.
Quick Guide to Frontal Hair Thinning Causes
| Cause | What It Is | Who It Affects Most |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia) | An inherited sensitivity of hair follicles to the hormone DHT, causing them to shrink over time. | Men with a family history of male pattern baldness. It's the most common cause by a wide margin. |
| Hormonal Changes | Fluctuations in hormones, especially the conversion of testosterone to DHT, directly impact hair growth cycles. | Primarily men, often starting anytime after puberty and progressing with age. |
| Lifestyle & Stress | Severe stress or poor nutrition can trigger temporary shedding (telogen effluvium), which can sometimes unmask underlying genetic thinning. | Anyone, but it's usually temporary. Chronic stress can sometimes accelerate genetic hair loss. |
Understanding that genetics and hormones are the main drivers is the first real step toward finding a solution that actually works. It helps explain why some treatments are effective and others are just wishful thinking.
For a more in-depth look at this, our guide on frontal hair thinning in males offers more specific insights.
How Genes and Hormones Team Up Against Your Hairline
Ever wonder why your hairline is often the first place to show signs of thinning? It’s not just random bad luck. There’s a powerful partnership at play between your genetics and your hormones—a biological story that unfolds right on your scalp.
And no, it's not just about getting older. It all comes down to a specific genetic blueprint you’ve inherited. Time to toss out that old myth that you only need to look at your mother’s father; the genes responsible for hair loss can come from either side of your family tree.
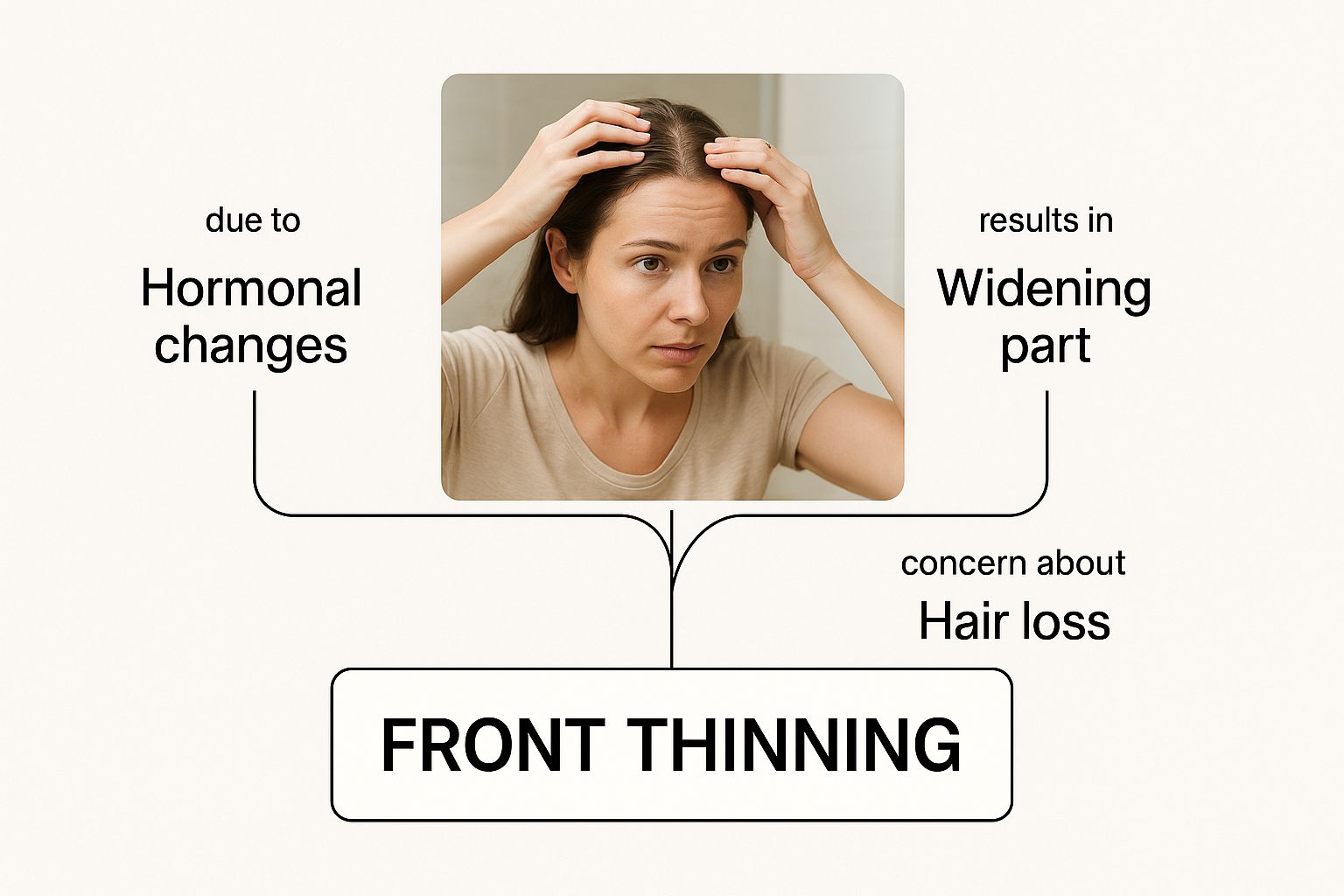
This is the classic "uh-oh" moment for so many people—noticing the thinning right at the forehead. This happens because the follicles in that specific area are ground zero for the genetic and hormonal interplay that drives hair loss.
Meet DHT: The Hormone Behind Hair Loss
The primary culprit in this story is a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Think of DHT as a potent, super-charged version of testosterone. It's created when testosterone meets an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase. While DHT is crucial for development earlier in life, it becomes a problem for hair follicles that are genetically programmed to be sensitive to it.
Imagine your hair follicles are like tiny locks, and DHT molecules are the keys. For most people, these keys don't fit the locks on their scalp. But for those with androgenetic alopecia (pattern hair loss), the follicles at the front of the scalp have locks that are a perfect match for the DHT key.
When DHT latches onto these specific follicles, it sends a destructive signal. This is the core mechanism explaining why your hair is thinning right at the front.
Here's the key takeaway: You don't necessarily have more DHT than someone with a full head of hair. The real issue is that your follicles are simply more sensitive to its effects. It's all about genetic sensitivity, not a hormonal imbalance.
This sensitivity isn't spread evenly across your head. The follicles on the back and sides of your scalp are typically resistant to DHT’s assault, which is why that hair often stays thick even as the hairline and crown thin out.
Miniaturization: How Follicles Shrink Over Time
Once DHT attaches to a sensitive follicle, it kicks off a process called miniaturization. Picture a healthy, thriving plant that suddenly starts getting less and less water. Over time, that plant would shrink, its leaves would get smaller, and eventually, it might stop growing entirely.
That’s exactly what happens to your hair follicles. Miniaturization is a slow, gradual decline that happens with each passing hair cycle.
Here's a breakdown of how it works:
- Shorter Growth Phase: DHT cuts the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle short. This gives the hair less time to grow long and strong before it sheds.
- Thinner Hairs: With every new cycle, the hair that the follicle produces becomes progressively finer, shorter, and lighter in color. This is why you see "thinning" instead of sudden bald patches.
- Dormant Follicles: Eventually, the follicle shrinks so much that it can no longer produce a visible hair. It goes dormant, and that's when you start to see a receding hairline or thinning patch.
This slow-motion shrinking is why frontal thinning can be so subtle at first, only becoming truly noticeable after a significant number of follicles are already affected. Getting a handle on these underlying factors is the first big step, and you can dive even deeper into the specific male pattern baldness causes in our detailed guide. It's this biological process that effective treatments are designed to stop in its tracks.
When It's More Than Just Genetics
While genes and hormones are the main characters in the story of a thinning hairline, they don't always act alone. Think of your genetic predisposition like a field of dry grass. It's ready to burn, but it often needs an outside spark to actually catch fire. Your overall health, stress levels, and daily habits can be that spark, either kicking off the thinning process or hitting the accelerator on it.
For a lot of people, the answer to "Why is my hair thinning in the front?" is more complicated than just shrugging and blaming their family tree. Several other factors can throw your hair's natural growth cycle out of whack, making an already vulnerable hairline look noticeably thinner.
The Role of Medical Conditions
Certain health issues can really throw a wrench in the works, and your hair is often one of the first places you'll see the fallout. When your body is fighting a battle on the inside, it smartly diverts energy away from things it deems non-essential—like growing strong, healthy hair.
Here are a few potential culprits to consider:
- Thyroid Disorders: Your thyroid is basically the master control panel for your metabolism. When it’s out of balance—either underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism)—it can mess with your hormones and disrupt the hair growth cycle. This often leads to diffuse shedding all over, which can make any frontal thinning look much worse.
- Anemia: Low iron is a big one. Anemia means your body isn't making enough red blood cells to ferry oxygen where it needs to go. Hair follicles are high-energy factories that crave oxygen, and when their supply gets choked off, hair production grinds to a halt.
- Autoimmune Responses: In conditions like alopecia areata, the body’s own immune system gets confused and mistakenly attacks its hair follicles. While this is famous for causing distinct round bald patches, it can sometimes show up as more generalized thinning right at the front.
It’s crucial to remember that while androgenetic alopecia is behind the lion's share of cases, these other medical issues absolutely can cause frontal hair loss. Plus, lifestyle factors like a poor diet, smoking, or even environmental toxins can team up with your genes to worsen follicle miniaturization. You can learn more about the global rates of baldness and contributing factors on Hairfixmexico.com.
When Stress Becomes a Factor
You’ve probably heard that stress makes your hair fall out, and it's not just an old wives' tale. Intense physical or emotional stress—we’re talking major surgery, a sudden loss, or a period of crushing pressure—can shock a huge number of your hair follicles, pushing them all into the shedding phase at once.
This phenomenon has a name: telogen effluvium.
Instead of losing the normal 50-100 hairs a day, you might suddenly start shedding 300 or more. This shedding happens all over your scalp, but it causes a dramatic drop in overall density, which can make a genetically receding hairline seem to fall back almost overnight.
The good news? Telogen effluvium is usually temporary. Once the stressor is gone and your body finds its footing again, the hair growth cycle typically resets within a few months. But for someone already fighting pattern baldness, it can feel like a massive and demoralizing setback.
How Your Habits Can Hurt Your Hairline
Finally, let’s talk about your daily routines. Some of them might be putting constant physical strain on the hair at the front of your scalp, leading to a condition called traction alopecia. This type of hair loss isn't caused by hormones or illness; it’s caused by repetitive, long-term pulling on the hair follicles.
This isn't about being a little rough with your comb one time. It's the result of consistent tension over months and years.
Common causes of traction alopecia include:
- Tight Hairstyles: Think tight ponytails, braids, cornrows, or buns that pull the hairline backward day after day.
- Restrictive Headwear: Constantly wearing tight hats, helmets, or headbands that rub and pull at the very same spot.
- Hair Extensions: Heavy or poorly installed extensions can place a surprising amount of weight on your natural hair roots, leading to breakage and follicle damage.
This constant mechanical stress can physically injure the follicles so badly that they eventually give up and stop producing hair for good. If your hairline is already thinning from genetics, this added physical strain is the absolute last thing it needs. Recognizing these controllable factors is a powerful first step in protecting the hair you still have.
Getting a Clear Diagnosis for Your Hair Thinning
Trying to figure out why your hair is thinning on your own can feel like chasing ghosts. One quick search online, and you're flooded with a dozen possible causes, leaving you more stressed out than when you started. That's why getting a professional diagnosis isn't just a suggestion—it's the single most important first step you can take. It’s the only way to find a treatment that will actually work.
Your best bet is to see a dermatologist who focuses on hair loss or a certified trichologist. These are the experts who understand the science of the hair and scalp. They have the tools and training to dig deep and find the real root of the problem.

What to Expect at Your Consultation
It's totally normal to feel a bit anxious before that first appointment, so let's walk through what typically happens. Think of the consultation as a mix of good old-fashioned detective work and medical science.
First, you'll talk. A lot. Your specialist will want to know everything—your family's history with hair loss, what you eat, your stress levels, any recent health issues, and the medications you're on. This conversation is full of crucial clues that help them pinpoint whether the cause is genetic, lifestyle-based, or something else.
Then comes the physical exam, and it’s more than just a quick look. They’ll likely use a dermatoscope, which is basically a high-powered magnifying glass for your scalp. This lets them see things the naked eye can't, like follicle miniaturization (a key sign of pattern baldness), inflammation, or other scalp conditions.
The whole point of a professional diagnosis is to stop guessing. It takes you from a vague worry like "my hair is thinning" to a concrete diagnosis like "you have stage 3 androgenetic alopecia with a contributing vitamin D deficiency."
Using Diagnostic Tools and Tests
To get the complete story, your doctor might suggest a few more tests. These aren't always needed, but they're invaluable for ruling out sneaky underlying health problems that can mimic pattern hair loss.
Here are a few common diagnostic tools:
- Blood Tests: A simple blood draw can reveal a lot. It checks for common culprits like iron deficiency (anemia), thyroid problems, and low levels of key vitamins like D and B12.
- The Pull Test: This sounds simple, but it's effective. The doctor will gently tug on a small group of about 40-60 hairs. If more than a handful come out, it could point to an active shedding condition like telogen effluvium.
- Scalp Biopsy: This is less common. If the diagnosis is particularly tricky, a tiny piece of scalp tissue might be taken for analysis in a lab. It’s usually reserved for situations where a scarring or autoimmune condition is suspected.
Understanding the Norwood Scale
For men dealing with genetic hair loss, specialists have a standardized guide called the Norwood scale. You can think of it as a roadmap that charts the typical progression of male pattern baldness through seven distinct stages.
Figuring out your stage on the Norwood scale does a few important things. It helps confirm the diagnosis, gives an idea of how the hair loss might progress, and sets a clear benchmark to measure whether a treatment is working. It also helps you and your doctor decide on the best game plan, because learning how to stop a receding hairline is different at stage 2 versus stage 5.
Ultimately, a solid diagnosis is the bedrock of any successful treatment plan. It keeps you from spinning your wheels—and wasting your money—on things that don't target the actual problem.
Finding a Treatment That Actually Works for You
Once you know what you’re dealing with, you can finally shift from worrying to taking action. The world of hair loss treatments can feel like a maze, but the good news is there are more genuinely effective options today than ever before. The whole game is about matching the right solution to the root cause of your hair thinning.
The goal isn't just to slam the brakes on hair loss; it's about building a strategy that fits your life, your budget, and what you hope to achieve. Let's walk through the most common and proven approaches so you can make a decision you feel confident about.
FDA-Approved Medical Treatments
When you’re up against androgenetic alopecia, the main battle is against DHT. Luckily, we have clinically proven medications designed to do exactly that, and they've become the foundation of treatment for millions of men.
-
Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine): This is often the first place people start. You apply it directly to your scalp, and it works as a vasodilator. That’s just a fancy way of saying it widens the blood vessels. Think of it like opening up a clogged highway, letting more blood, oxygen, and nutrients rush to your struggling hair follicles. This surge of circulation can wake up dormant follicles and help them produce thicker hair again. It's available over-the-counter and most people tolerate it well.
-
Oral Finasteride (Propecia): This is a prescription pill that goes straight to the source of the problem. Finasteride works by blocking the 5-alpha reductase enzyme—the exact enzyme that turns testosterone into the follicle-shrinking DHT. By dramatically lowering DHT levels in your scalp, it can stop the miniaturization process cold and, for many guys, even bring about some impressive regrowth.
These two are often used together, creating a powerful one-two punch that fights genetic hair loss from both the outside-in and the inside-out.
Advanced Therapies and Regenerative Medicine
Moving beyond daily meds, there are several in-office procedures that use your body's own healing powers to kickstart hair growth. These are fantastic options if you’re looking for a more hands-on approach.
One of the most exciting non-surgical treatments is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy. This method taps into the incredible healing power packed inside your own blood. We take a small blood sample, spin it in a centrifuge to separate and concentrate the platelets, which are little powerhouses of growth factors.
This super-concentrated plasma is then carefully injected back into the areas of your scalp where you see thinning. The idea is to send a powerful "wake-up call" to those shrinking follicles, triggering tissue repair and pushing them back into an active growth phase.
A lot of people are drawn to this because it's a completely natural approach—no synthetic chemicals or daily pills involved. To really get a feel for the science behind it, you can explore this detailed overview of PRP for hair loss treatment to see if it’s a good fit.
Another popular choice is Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT). This usually involves wearing a cap, comb, or headband that emits red light. The energy from the light gets absorbed by your scalp cells, which can help ramp up cellular activity and blood flow, creating a much healthier environment for your hair to grow.
Surgical and Cosmetic Solutions
For those with more advanced hair loss or anyone who wants a permanent, game-changing result, a hair transplant is still the gold standard.
-
Hair Transplants: Modern techniques like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) are incredible. A surgeon moves individual, DHT-resistant hair follicles from the back and sides of your head to the thinning areas up front. They're essentially "replanting" your own healthy hair to rebuild your hairline. The results are permanent and, when done well, look completely natural.
-
Cosmetic Options: If you want an immediate confidence boost, scalp micropigmentation (SMP) or high-quality hair fibers can create the illusion of more density. SMP is basically a specialized cosmetic tattoo that mimics the look of tiny hair follicles, which does a great job of reducing the contrast between your hair and scalp.
And for anyone who wants to support their medical treatments with natural care, this ultimate guide to hair oiling for hair growth offers some great tips on improving hair health the old-fashioned way.
To help put all this into perspective, here’s a quick comparison of the most popular options.
Comparing Popular Frontal Hair Loss Treatments
Navigating the options can be tough, so this table breaks down the most common treatments to help you see how they stack up against each other.
| Treatment Type | How It Works | Best For | Typical Time to See Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Minoxidil | Increases blood flow to follicles, promoting a healthier growth environment. | Early-to-moderate thinning; works well for both frontal and crown areas. | 3-6 months of consistent use. |
| Oral Finasteride | Reduces scalp DHT levels to stop or reverse follicle miniaturization. | Men with genetic pattern hair loss who want to address the hormonal cause. | 3-6 months, with full effect often seen after a year. |
| PRP Therapy | Injects growth factors from your own blood to stimulate dormant follicles. | Individuals with early-to-moderate thinning seeking a regenerative approach. | A series of treatments over 3-6 months. |
| Hair Transplant | Surgically moves DHT-resistant follicles to thinning areas for permanent regrowth. | Those with stabilized, more advanced hair loss and a healthy donor area. | 6-12 months for the full, final result. |
Ultimately, the best path forward is the one that targets the specific cause of your hair loss and fits realistically into your life.
Frequently Asked Questions

Even after diving into the science of why hair thins at the front, it's completely normal to still have some lingering questions. Let's tackle a few of the most common ones so you can move forward with total clarity.
Can Stress Alone Make My Hair Thin Only in the Front?
It's highly unlikely. Severe stress typically triggers a condition called telogen effluvium, which causes diffuse hair shedding all over your head, not just in one specific spot.
However, stress is a powerful accelerator. Think of it like this: if your genetic predisposition to frontal thinning is a smoldering ember, a major life stressor is like pouring gasoline on it. It won't start the fire, but it can absolutely make it flare up and become noticeable much faster.
Will My Hair Grow Back if I Just Improve My Diet?
That really depends on what’s causing the thinning in the first place. If a specific nutritional deficiency, like low iron, is the main culprit, then yes—correcting that deficiency with a better diet can absolutely lead to regrowth.
But for genetic hair loss (androgenetic alopecia), diet plays a supporting role, not the lead. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet is crucial for the health of the hair you still have and might help slow the thinning process. For real, meaningful regrowth at the hairline, though, it usually needs to be combined with proven medical treatments.
A good diet is a crucial supporting actor, but it's rarely the star of the show when it comes to reversing genetic hair loss.
If you're looking for a comprehensive game plan, understanding the full range of options for how to stop balding can give you a much clearer picture.
Are Natural Remedies Like Rosemary Oil Proven to Work?
Some natural remedies, especially rosemary oil and saw palmetto, have shown some interesting results in smaller-scale studies. The theory is that they might have a mild effect on DHT activity right at the scalp.
That said, the scientific evidence backing them up isn't anywhere near as robust as it is for FDA-approved treatments like Minoxidil and Finasteride. It’s best to think of them as complementary therapies—something you might add to your routine—rather than a primary line of defense against significant frontal thinning. Always chat with your doctor before starting any new supplements.
At What Age Does Frontal Hair Thinning Usually Start?
There’s no magic number here; it all comes down to your personal genetic blueprint. For some men with a strong genetic tendency, the first signs of a receding hairline can pop up in their late teens or early 20s.
For many others, it might not become a concern until their 30s, 40s, or even later. The important thing isn't the age on your driver's license, but rather catching the pattern of change when it starts for you. The sooner you notice it, the more effective any intervention will be.
At PRP For HairLoss, we believe that clear, honest information is the first step toward reclaiming your confidence. If you're ready to move from questions to answers, explore our resources to understand advanced treatments like PRP. Visit us at https://prpforhairloss.com to learn more.

Leave a comment