Let's get straight to the heart of the matter. For most men, hair loss boils down to a one-two punch of your genes and your hormones. This combination is known as androgenetic alopecia, or what we commonly call male pattern baldness.
Think of it this way: your genetics hand your hair follicles a script, detailing how they should behave over time. Then, your hormones act out that script, triggering the gradual process of thinning and recession.
Decoding the Triggers Behind Hair Loss

Trying to figure out what's causing your hair loss can feel like you're untangling a knotted fishing line. While your family tree is almost always the main suspect, it’s rarely the only factor at play. The journey toward a receding hairline or a thinning crown is often influenced by a whole host of internal and external forces.
Losing your hair is an incredibly common part of the male experience. Worldwide, about 85% of men will deal with significant thinning at some point. Of those cases, androgenetic alopecia is responsible for a staggering 95%. This makes perfect sense when you learn that over 70% of people with hair loss have a family history of it. If you want to dive deeper into the numbers, you can review the latest hair loss statistics to see the full picture.
A Snapshot of Hair Loss Causes
To make things clearer, we can sort the causes into four main buckets. Each one has a different role to play, and sometimes they overlap, which is why figuring out the root cause can feel like a process of elimination.
- Genetic and Hormonal Factors: This is the big one. It’s all driven by a hereditary sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a powerful male hormone.
- Medical Conditions: Sometimes, your hair is just the messenger. Underlying health problems like thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, or even a bad infection can throw your hair's growth cycle completely off track.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Stressors: Things like chronic stress, a poor diet lacking key nutrients, and even pulling your hair back too tight can lead to shedding. This can be temporary or, in some cases, permanent.
- Medications and Treatments: It’s no secret that some medical treatments, like chemotherapy, cause hair loss. But other common prescription drugs can also have hair shedding as a side effect.
Key Takeaway: While male pattern baldness is what most guys have, don't just assume that's what's happening to you. Any sudden or patchy hair loss could be your body's way of signaling that something else is going on. Telling the difference is the first critical step toward finding a solution that actually works.
To help you get a clearer picture, I've put together a quick summary table. It breaks down the primary triggers so you can see which factors might be at play in your own situation.
Primary Hair Loss Triggers at a Glance
| Cause Category | Primary Driver | Common Examples | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic & Hormonal | Sensitivity to DHT | Male Pattern Baldness | Very High (95% of cases) |
| Medical Conditions | Systemic health issues | Thyroid Disease, Alopecia Areata | Moderate to Low |
| Lifestyle & Diet | External pressures | High Stress, Poor Nutrition | Variable |
| Medications | Drug side effects | Chemotherapy, Blood Pressure Meds | Low (Varies by drug) |
This table gives you a bird's-eye view of the landscape, showing how different factors contribute to hair loss. While genetics are the dominant force, it's worth understanding the other potential causes, especially if your hair loss doesn't fit the typical pattern.
Your Genes and Hormones: The Inside Story
To really get to the bottom of what causes hair loss for most guys, we have to look under the hood. It’s all about the intricate dance between your genetics and your hormones. For the vast majority of men, the main driver is a condition called androgenetic alopecia—and it’s fueled entirely by that powerful duo.
Think of your DNA as the master blueprint for your hair. This blueprint holds very specific instructions for every single hair follicle on your head. For some of us, those instructions include a built-in sensitivity to certain hormones. It’s like a pre-programmed vulnerability just waiting for the right trigger to come along.
The Role of DHT in Hair Loss
That trigger is a potent male hormone, or androgen, called dihydrotestosterone, better known as DHT. Your body naturally converts testosterone into DHT using a specific enzyme. While DHT is absolutely essential for male development during our younger years, it can become a real problem for genetically susceptible hair follicles as we get older.
This is where that genetic script flips on. If your hair follicles are programmed to be sensitive to DHT, the hormone latches onto receptors within them and kicks off a process called miniaturization.
The Shrinking Factory Analogy: Imagine each hair follicle is a tiny, bustling factory that produces a strong, healthy strand of hair. When DHT shows up, it’s like someone sneaks into the control room and starts dialing down the factory's output. With every new hair growth cycle, the factory itself gets a little smaller.
Over time, this "shrinking factory" starts producing weaker and weaker products. The hair strands that do grow become shorter, finer, and even lighter in color. Eventually, the factory just shuts down for good, and that follicle stops producing hair entirely. This gradual shutdown is what creates the classic patterns of male baldness, from a receding hairline to a thinning spot on the crown.
Debunking a Common Genetic Myth
There’s a stubborn old myth that says the baldness gene comes only from your mother's side. While it's true that a major gene linked to androgenetic alopecia is on the X chromosome (which you get from your mom), it’s far from the only one.
Modern science has actually pinpointed numerous other genes on different chromosomes that also contribute. What does this mean for you? You can inherit the tendency for hair loss from either or both of your parents. If you look at your family tree and see baldness on any of the branches, your own risk goes up.
The infographic below shows how various hormonal factors, especially the critical androgen DHT, influence hair growth.
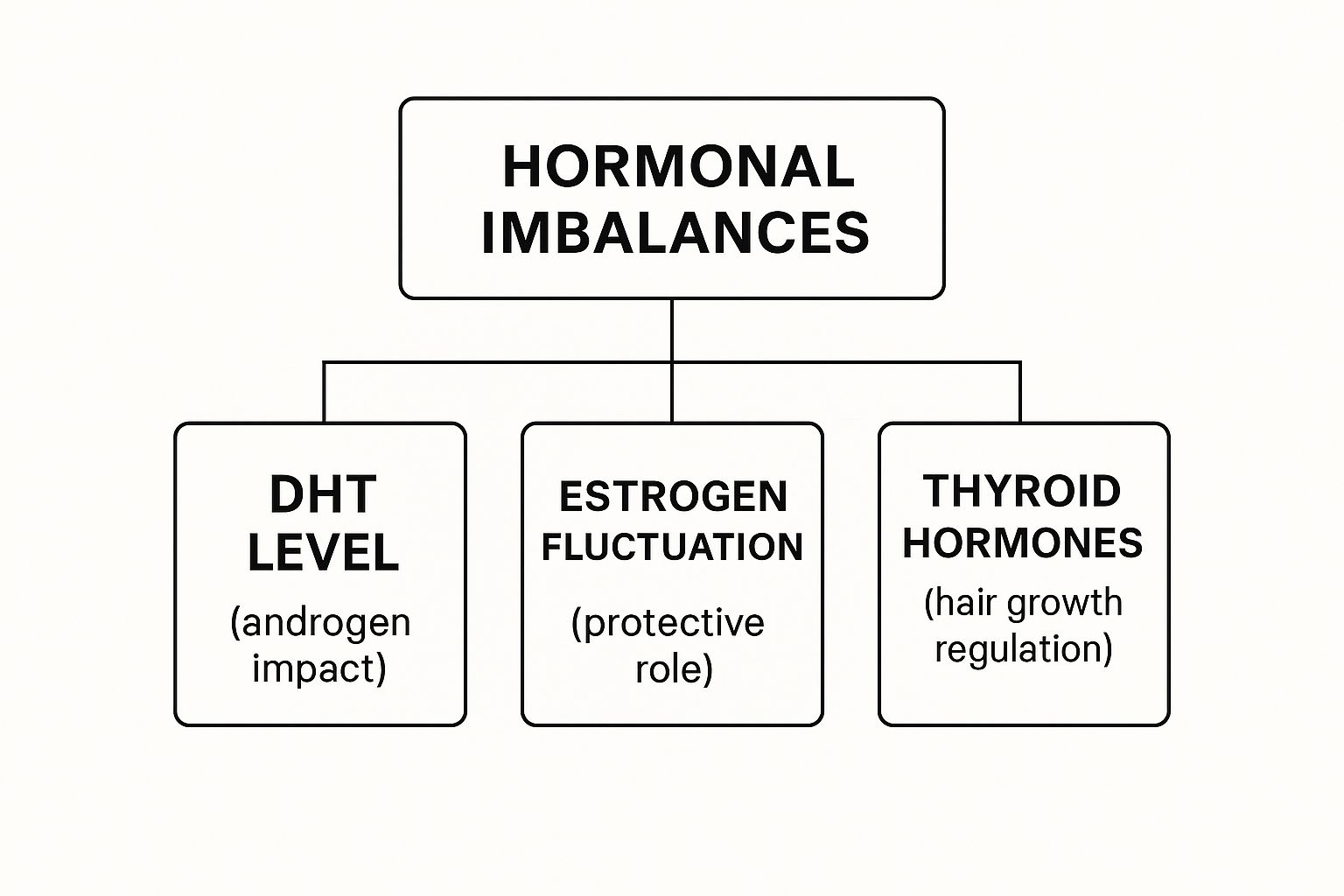
As the diagram shows, while DHT is a major player, other hormones like those from the thyroid and even estrogen play a role in regulating the complex hair growth cycle.
Hormonal Influences Beyond DHT
DHT may be the main character in the story of male pattern baldness, but it isn’t the only hormonal actor on stage. Other hormonal shifts can throw a wrench in your hair's health and growth cycle, too.
Two other key players to be aware of are:
- Thyroid Hormones: When your thyroid is out of whack—whether it's overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism)—it can wreak havoc on your hair. This usually causes a diffuse thinning all over your scalp, rather than the distinct pattern seen with DHT.
- Cortisol: We all know cortisol as the "stress hormone." When its levels are chronically high, it can push a huge number of hair follicles into the shedding phase all at once. This leads to a condition called telogen effluvium, where you'll notice significant, widespread shedding.
These factors help explain why the answer to "what causes hair loss?" is often more complex than it seems. While androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is by far the most common cause, accounting for around 95% of hair loss cases, other issues can exist right alongside it or act as separate triggers. For instance, autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata, which affects roughly 160 million people worldwide, represent a completely different pathway to hair loss. You can explore more data on the global hair thinning market to see how these trends are shaping up.
Grasping this core biological process is the first, most crucial step toward finding solutions that actually work. Once you recognize that your hair loss is likely the result of a genetic predisposition being triggered by hormonal actions, you're in a much better position to navigate the treatment options and make smart decisions for your hair.
Medical Conditions That Can Trigger Hair Loss

While your genes and hormones are the usual suspects in male hair loss, your hair often acts as a barometer for your overall health. Sometimes, seeing more hair in the drain isn't about your family tree—it's your body's way of signaling that something else is going on under the surface.
Think of it this way: your body is a complex, interconnected system. When one part of that system gets thrown out of whack, the effects can ripple outwards. Your hair is often one of the first and most visible places you'll see those changes.
The Great Disruption: Telogen Effluvium
Have you ever gone through a major illness, a surgery, or a period of extreme stress, only to find yourself shedding a shocking amount of hair a few months later? That's likely telogen effluvium, and it's not a disease but a temporary reaction to a shock.
Here's what happens. Your hair follicles normally cycle through a growth phase and a resting (telogen) phase. A major stressor—physical or emotional—can send a distress signal throughout your body, pushing a huge number of hair follicles, sometimes up to 70%, into the resting phase all at once. A few months down the line, all that hair that went into hibernation starts to shed, and the thinning becomes obvious.
The good news? This is almost always a temporary state of affairs. Once the stressor is resolved and your body gets back on track, your hair growth cycle usually normalizes within six to nine months.
When Your Own Body Is the Attacker
Another major player in non-pattern hair loss is alopecia areata, which is an autoimmune disease. In simple terms, your immune system gets its wires crossed and mistakenly identifies your own hair follicles as a threat.
It then launches an attack, creating inflammation that shuts down the follicle and causes hair to fall out suddenly. This often shows up as smooth, round, coin-sized bald patches, but it can sometimes be more widespread. This process is worlds away from the slow, hormonal miniaturization of male pattern baldness.
Key Insight: Alopecia areata is a prime example of how internal systems can directly sabotage hair. It’s not about hormones; it’s your body's own defense team mistakenly turning on you.
For some people, the hair grows back without any intervention, but for others, it can be a frustrating, recurring issue. That’s why getting a firm diagnosis from a dermatologist is so critical to understanding what’s really happening and finding the right path forward.
Thyroid Imbalances and Scalp Health
Your thyroid, the small butterfly-shaped gland in your neck, is your body's master metabolic regulator. If it produces too much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or too little (hypothyroidism), it can throw nearly every system out of balance—and that absolutely includes your hair growth cycle.
Unlike the predictable pattern of a receding hairline or thinning crown, thyroid-related hair loss typically shows up as diffuse thinning all over your head. It’s a classic sign that your internal chemistry is off.
On top of that, the health of your scalp itself can create an environment that’s either hostile or helpful to hair growth. Problems can include:
- Fungal Infections: An infection like tinea capitis, also known as scalp ringworm, can invade the hair shaft, causing inflammation, scaly patches, and patches of hair loss.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This is a very common condition that leads to red, itchy, and flaky skin (think stubborn dandruff). When it gets severe, the inflammation can disrupt the hair follicles and contribute to shedding.
These issues really drive home the importance of scalp health. A healthy scalp is the foundation for healthy hair. When that foundation is compromised by infection or inflammation, hair loss is often the result. If you notice sudden changes, patchy loss, or any kind of scalp discomfort, it's time to see a doctor.
How Your Lifestyle and Diet Impact Hair Health
While your genes might load the gun for hair loss, it’s often your lifestyle and diet that pull the trigger. Think of it this way: genetics lays the foundation, but your daily habits are the builders. What you eat, how you manage stress, and even how you style your hair can either reinforce that foundation or cause it to crumble.
Your hair is a surprisingly accurate barometer of your internal health. If your body isn't getting what it needs, non-essential systems—like hair growth—are the first to be put on the back burner. Resources are sent to vital organs first, leaving your hair follicles to fend for themselves.
The Nutritional Foundation of Your Hair
Your hair is made of protein—specifically, a tough one called keratin. To build a strong keratin structure, your body's "hair factory" needs a steady assembly line of key vitamins and minerals. If those raw materials are missing, production grinds to a halt, resulting in weak, brittle strands that shed easily.
These are a few of the non-negotiable nutrients for healthy hair:
- Iron: This is the workhorse mineral responsible for creating hemoglobin, which ferries oxygen to your cells. Without enough oxygen, the cells that power hair growth can't function properly, often leading to noticeable shedding.
- Zinc: Zinc is the repairman for your hair. It helps with tissue growth and ensures the oil glands around your follicles are working correctly. A deficiency can manifest as a dry, flaky scalp and thinning hair.
- Biotin (Vitamin B7): Known as one of the fundamental building blocks for keratin, biotin is crucial for hair strength and integrity. While a true deficiency is rare, not getting enough can compromise your hair's structure.
A well-rounded diet is about more than just general wellness; it's targeted fuel for your hair. For example, many foods that boost energy are naturally packed with the very nutrients your hair is craving.
Key Takeaway: You can't argue with your DNA, but you can absolutely control what's on your plate. A nutrient-rich diet is one of the most practical and powerful tools you have for supporting your hair from the inside out.
The Damaging Effects of Stress and Styling
Beyond your diet, two of the biggest lifestyle culprits behind hair loss are chronic stress and damaging styling habits. They attack your hair from different angles but can be equally destructive.
When you're constantly on edge, your body produces a flood of the stress hormone cortisol. Think of cortisol as an emergency signal that disrupts your hair's natural growth rhythm. It can prematurely shove a large number of follicles from their growing phase right into the shedding phase, triggering a condition called telogen effluvium, where you suddenly lose a lot more hair than usual.
At the same time, what you do to your hair on the outside matters just as much. Constant pulling and tension can lead to traction alopecia, a type of hair loss caused by physical stress on the follicles.
This is often the result of:
- Wearing tight ponytails, man buns, or braids day after day.
- Using heavy hair extensions that tug on your natural hair.
- Overdoing it with harsh chemical treatments or high-heat styling tools.
The good news is that this type of hair loss is often preventable and even reversible if you catch it early. But if you don't give your follicles a break, the damage can become permanent.
How Lifestyle Choices Affect Hair
The little choices you make every day add up. Poor sleep, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle create an internal environment that works against your hair. Smoking, for instance, constricts blood vessels, literally starving your scalp of the oxygen and nutrients it needs to thrive.
The table below breaks down how some common lifestyle factors can either help or harm your hair.
Lifestyle Factors and Their Effect on Hair
| Lifestyle Factor | Negative Impact (Contributes to Loss) | Positive Impact (Supports Growth) |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Lacks iron, zinc, protein | Rich in vitamins, minerals, protein |
| Stress | High cortisol disrupts growth cycles | Management techniques lower cortisol |
| Styling | Tight styles, harsh chemicals | Gentle handling, natural styles |
| Smoking | Restricts blood flow to scalp | Avoidance supports circulation |
| Sleep | Poor sleep raises stress hormones | Quality sleep aids cell repair |
In the end, your hair's health is a direct reflection of your overall wellness. By focusing on a nutrient-dense diet, finding healthy ways to manage stress, and treating your hair gently, you create the best possible conditions for it to grow strong and stick around for the long haul.
Hair Loss Around the World: A Global Perspective

When you're dealing with hair loss, it’s easy to feel isolated, as if you're the only one staring back at a changing hairline in the mirror. But the truth is, you're part of a massive global community. Hair loss is a shared human experience that transcends borders, cultures, and backgrounds, impacting hundreds of millions of people across the planet.
This isn't just a problem in one corner of the world; it’s a universal condition. The numbers alone paint a staggering picture. In the United States, an estimated 56 million people are affected by hair loss, with 35 million of them being men. Travel across the globe, and the scale becomes even more immense. China is grappling with the issue on a huge scale, with approximately 250 million individuals experiencing hair loss. You can dive deeper into these hair loss statistics to get a better sense of the full scope.
Cultural Views on Hair and Thinning
Of course, the raw numbers only tell part of the story. How people perceive and react to hair loss can be wildly different depending on their culture and society. These views shape everything from personal acceptance to how urgently someone might seek out a solution.
In some cultures, for instance, a thick head of hair is deeply intertwined with ideas of youth, vitality, and even social standing. In those places, men might feel a great deal of pressure to tackle thinning hair the moment it starts. In other parts of the world, balding might be seen as a natural, even distinguished, part of getting older—something to be accepted rather than fought.
Global Insight: The emotional and psychological weight of hair loss is something people feel everywhere, but the cultural reaction is far from uniform. Knowing this can help normalize your own experience; there's no single "right" way to feel or respond.
Understanding this global context is powerful. It reminds us that the root causes—genetics, hormones, lifestyle—are fundamental biological processes that connect men from all walks of life.
A Worldwide Phenomenon
The sheer prevalence of male hair loss really drives home just how common it is. A study in India, for example, found that a remarkable 63.2% of men between the ages of 21 and 61 were dealing with it. That’s an incredibly high figure and a clear sign of how widespread this experience is.
Seeing your own journey in this global light can be reassuring. You are far from alone in looking for answers and effective solutions. From London to Beijing, from Mumbai to New York, men are navigating the same challenges, driven by the very same biology. This shared experience highlights just how important it is for everyone to have access to reliable information and support.
When Should You See a Doctor About Hair Loss?
Trying to figure out what’s causing your hair loss can feel like a guessing game. While some gradual thinning is a normal part of life for many men, certain signs are your cue to stop speculating and get a professional opinion. Knowing when to move from anxiously checking the mirror to actually booking a doctor's appointment is the first real step toward finding a solution that works.
Losing 50 to 100 hairs a day is totally normal—it’s just part of your hair's natural growth and shedding cycle. You probably don't even notice it. The real moment to start paying attention is when you see a sudden jump in shedding or if the pattern of loss just seems… off.
Red Flags That Mean It's Time for a Professional Opinion
If your hair is thinning gradually in that classic pattern—a receding hairline and a thinning spot on top—you're most likely dealing with standard male pattern baldness. But if you notice any of the following, it’s a good idea to schedule a visit with a dermatologist or your family doctor. These symptoms can point to something else going on under the surface that needs a proper diagnosis.
Keep an eye out for these key warning signs:
- Sudden, Rapid Shedding: You’re suddenly finding a lot more hair on your pillow, in the shower drain, or on your brush. Some people describe this as their hair coming out in clumps or handfuls.
- Patchy Hair Loss: You’re discovering smooth, completely bald patches, often in a round or oval shape. This is a tell-tale sign of alopecia areata, which is an autoimmune condition.
- Scalp Discomfort: The hair loss comes with an itchy, burning, or painful scalp. If you see redness or scaling, it might signal an infection or an inflammatory skin issue.
- Widespread Thinning: Instead of a distinct pattern, your hair just seems to be thinning out all over your head. This kind of diffuse loss can be a sign of a condition called telogen effluvium or point to a bigger health problem.
Here's the bottom line: Pain, itching, or sudden bald patches aren't typical for male pattern baldness. Think of these as your body’s alarm bells, signaling that something more than just genetics is likely happening. Getting the right diagnosis is the absolute first step before you even think about treatment.
What to Expect During Your Consultation
Walking into a doctor's office to talk about hair loss can feel a bit daunting, but it's a pretty straightforward process aimed at getting to the bottom of things. A dermatologist will usually kick things off with a thorough chat about your medical history, your family's history with hair loss, your diet, and your daily lifestyle.
From there, they'll likely move on to a few key diagnostic steps:
- Scalp Examination: Your doctor will take a close look at your scalp, often using a special magnifying scope to check the health of your hair follicles and look for any signs of inflammation or infection.
- The Pull Test: It sounds simple because it is. The doctor will gently tug on a small group of hairs to see how many come loose. This quick test helps them gauge how severe the shedding is.
- Blood Tests: To rule out other potential causes, your doctor might order some blood work. This is to check for things like low iron or vitamin D, thyroid problems, or hormonal imbalances that could be contributing to your hair loss.
Taking this step puts you back in control. Instead of getting lost in a sea of online articles and potential causes, you'll walk out with a clear, evidence-based diagnosis. That clarity is the foundation for any successful treatment plan, whether that means fixing a vitamin deficiency, managing an underlying condition, or exploring options like those we cover on our blog at PRP for Hairloss.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hair Loss
Once you start digging into what causes hair loss, you’ll find yourself with a ton of questions. This topic is swimming with myths and half-truths, so let's cut through the noise and get you some straight answers.
Here are the questions we hear all the time, answered with the clarity you need.
Can Hair Loss Be Reversed?
This is the million-dollar question, isn't it? The honest answer is: it all comes down to the root cause. Whether or not your hair will grow back depends entirely on why you lost it in the first place.
Think of it this way: some hair loss is a temporary reaction, while other types are a permanent, progressive condition.
-
Often Reversible: Issues like telogen effluvium—hair loss triggered by major stress, a sudden illness, or even a nutrient deficiency—are usually temporary. Once you fix the underlying problem, like getting your stress under control or correcting low iron levels, your hair growth cycle typically resets. The shed hairs will grow back over the next several months.
-
Progressive & Manageable: Genetic hair loss (male pattern baldness) is a different beast. It's not a temporary hiccup; it's a continuous process where DHT slowly strangles your hair follicles. In this scenario, "reversal" isn't about resurrecting dead follicles on a slick-bald scalp. It's about stopping the thinning in its tracks and coaxing miniaturized, weakened follicles back to health with proven treatments.
The Bottom Line: With genetic hair loss, the goal is to save the hair you have, thicken up the thinning areas, and prevent more follicles from giving up. The sooner you start, the more hair you have to save.
Do Hair Growth Vitamins Actually Work?
They can, but with a huge asterisk. Hair growth vitamins are only effective if your hair loss is actually caused by a nutritional deficiency. If you're low on key nutrients like iron, zinc, or vitamin D, then yes, supplementing can absolutely help your hair grow back normally by filling that gap.
Here’s what they can't do: Vitamins are not a cure for male pattern baldness. Genetic hair loss is a hormonal problem, not a nutritional one. A good multivitamin is great for your overall health (and healthy hair, by extension), but it won't do a thing to block the damaging effects of DHT on your follicles. Popping extra biotin won't stop a receding hairline that's written into your DNA.
At What Age Does Hair Loss Usually Start?
We tend to picture hair loss as a middle-aged problem, but for a lot of guys, the genetic clock starts ticking much earlier. There’s really no set age for male pattern baldness to kick in—it all boils down to your personal genetics and your body's sensitivity to hormones.
For many men, the first subtle signs of thinning or a receding hairline pop up in their late twenties or thirties. But it's not at all rare for it to start in the late teens or early twenties. In fact, an earlier start often signals a more aggressive pattern of loss down the road. On the other hand, some guys might not notice any real thinning until they hit their 40s or 50s.
Ultimately, it’s a genetic lottery. If baldness runs strong and started early in your family, your chances of seeing it at a younger age are much higher.
Trying to figure out hair loss can feel like a maze, but getting straight facts is the first step toward a real solution. At PRP For HairLoss, we focus on giving you clear, evidence-based information on treatments like PRP so you can make a decision that's right for you. To find out more, explore our resources at https://prpforhairloss.com.
Leave a comment